What Is The Point Of Double Buffering In Registers
Buffering in Operating System
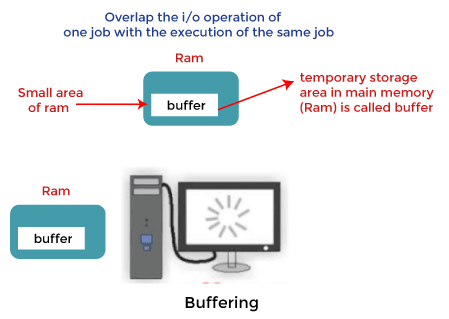
The buffer is an surface area in the main memory used to shop or hold the data temporarily. In other words, buffer temporarily stores information transmitted from i place to another, either betwixt two devices or an application. The deed of storing data temporarily in the buffer is called buffering .
A buffer may be used when moving data betwixt processes within a computer. Buffers can be implemented in a fixed memory location in hardware or by using a virtual information buffer in software, pointing at a location in the physical memory. In all cases, the information in a data buffer are stored on a physical storage medium.
Virtually buffers are implemented in software, which typically uses the faster RAM to shop temporary data due to the much faster access time than hard disk drives. Buffers are typically used when in that location is a divergence between the charge per unit of received data and the charge per unit of processed data, for example, in a printer spooler or online video streaming.
A buffer oft adjusts timing by implementing a queue or FIFO algorithm in memory, simultaneously writing data into the queue at i charge per unit and reading it at another charge per unit.
Purpose of Buffering
You face buffer during watching videos on YouTube or live streams. In a video stream, a buffer represents the amount of data required to exist downloaded before the video can play to the viewer in real-time. A buffer in a estimator surroundings means that a set amount of data will be stored to preload the required information earlier information technology gets used by the CPU.
Computers take many different devices that operate at varying speeds, and a buffer is needed to act every bit a temporary placeholder for everything interacting. This is washed to keep everything running efficiently and without problems between all the devices, programs, and processes running at that time. There are three reasons behind buffering of data,
- It helps in matching speed between ii devices in which the data is transmitted. For instance, a hard disk has to store the file received from the modem. As we know, the transmission speed of a modem is deadening compared to the hard deejay. So bytes coming from the modem is accumulated in the buffer space, and when all the bytes of a file has arrived at the buffer, the entire data is written to the hard disk in a single operation.
- It helps the devices with dissimilar sizes of data transfer to go adapted to each other. It helps devices to manipulate information before sending or receiving it. In calculator networking, the large message is fragmented into minor fragments and sent over the network. The fragments are accumulated in the buffer at the receiving cease and reassembled to form a complete large bulletin.
- It also supports re-create semantics . With copy semantics, the version of data in the buffer is guaranteed to be the version of data at the fourth dimension of system call, irrespective of any subsequent change to data in the buffer. Buffering increases the performance of the device. It overlaps the I/O of ane job with the computation of the same job.
Types of Buffering
There are three master types of buffering in the operating organization, such every bit:
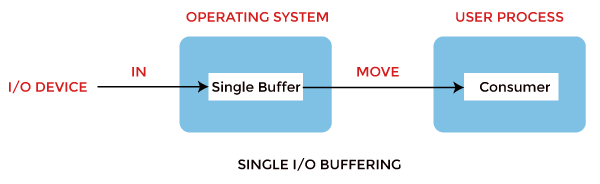
i. Single Buffer
In Single Buffering, simply one buffer is used to transfer the information betwixt ii devices. The producer produces one block of data into the buffer. Later that, the consumer consumes the buffer. Only when the buffer is empty, the processor once again produces the data.
Cake oriented device: The following operations are performed in the block-oriented device,
- System buffer takes the input.
- Afterward taking the input, the block gets transferred to the user space and then requests another cake.
- 2 blocks piece of work simultaneously. When the user processes one block of data, the next block is being read in.
- Bone tin swap the processes.
- Bone tin record the data of the system buffer to user processes.
Stream oriented device: It performed the following operations, such as:
- Line -at a time operation is used for scroll made terminals. The user inputs one line at a time, with a railroad vehicle return waving at the end of a line.
- Byte -at a time performance is used on forms mode, terminals when each keystroke is pregnant.
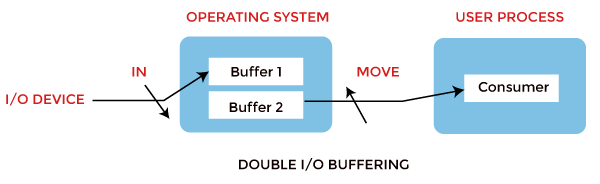
ii. Double Buffer
In Double Buffering, two schemes or two buffers are used in the place of i. In this buffering, the producer produces i buffer while the consumer consumes another buffer simultaneously. And so, the producer not needs to wait for filling the buffer. Double buffering is also known every bit buffer swapping.
Block oriented: This is how a double buffer works. There are two buffers in the system.
- The driver or controller uses ane buffer to shop information while waiting for information technology to be taken by a higher hierarchy level.
- Some other buffer is used to store data from the lower-level module.
- A major disadvantage of double buffering is that the complexity of the process gets increased.
- If the process performs rapid bursts of I/O, and then using double buffering may exist scarce.
Stream oriented: Information technology performs these operations, such every bit:
- Line - at a fourth dimension I/O, the user process does non demand to exist suspended for input or output unless the procedure runs ahead of the double buffer.
- Byte - at fourth dimension operations, double buffer offers no advantage over a unmarried buffer of twice the length.
three. Circular Buffer
When more than than two buffers are used, the buffers' collection is called a circular buffer. Each buffer is being i unit of measurement in the circular buffer. The information transfer rate will increment using the circular buffer rather than the double buffering.
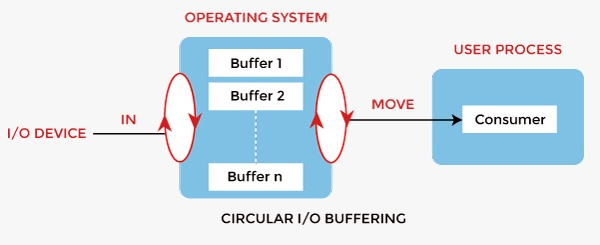
- In this, the information do not directly pass from the producer to the consumer because the data would change due to overwriting of buffers before consumed.
- The producer can just make full up to buffer x-1 while data in buffer x is waiting to exist consumed.
How Buffering Works
In an operating organisation, buffer works in the following fashion:
- Buffering is done to deal effectively with a speed mismatch between the producer and consumer of the data stream.
- A buffer is produced in the main retentivity to heap upwards the bytes received from the modem.
- Later receiving the data in the buffer, the data go transferred to a disk from the buffer in a single operation.
- This process of data transfer is non instantaneous. Therefore the modem needs another buffer to store additional incoming data.
- When the offset buffer got filled, then it is requested to transfer the data to disk.
- The modem then fills the additional incoming data in the second buffer while the information in the showtime buffer gets transferred to the deejay.
- When both the buffers completed their tasks, the modem switches back to the first buffer while the information from the 2d buffer gets transferred to the disk.
- Two buffers atomize the producer and the data consumer, thus minimising the time requirements between them.
- Buffering also provides variations for devices that take different information transfer sizes.
Advantages of Buffer
Buffering plays a very important role in any operating system during the execution of any process or task. Information technology has the following advantages.
- The utilize of buffers allows compatible disk access. It simplifies system pattern.
- The organization places no information alignment restrictions on user processes doing I/O. By copying data from user buffers to system buffers and vice versa, the kernel eliminates the need for special alignment of user buffers, making user programs simpler and more portable.
- The use of the buffer can reduce the amount of deejay traffic, thereby increasing overall system throughput and decreasing response fourth dimension.
- The buffer algorithms help ensure file system integrity.
Disadvantages of Buffer
Buffers are non improve in all respects. Therefore, in that location are a few disadvantages as follows, such as:
- It is plush and impractical to have the buffer be the verbal size required to hold the number of elements. Thus, the buffer is slightly larger most of the fourth dimension, with the rest of the space beingness wasted.
- Buffers have a stock-still size at whatever point in time. When the buffer is total, it must be reallocated with a larger size, and its elements must exist moved. Similarly, when the number of valid elements in the buffer is significantly smaller than its size, the buffer must exist reallocated with a smaller size and elements be moved to avoid too much waste.
- Use of the buffer requires an extra information copy when reading and writing to and from user processes. When transmitting large amounts of data, the extra copy slows downward functioning.
What Is The Point Of Double Buffering In Registers,
Source: https://www.javatpoint.com/buffering-in-operating-system
Posted by: robertsgoodst.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is The Point Of Double Buffering In Registers"
Post a Comment